- Products
- Reactive dyes
- Dye azides
- TAMRA azide, 5-isomer
TAMRA azide, 5-isomer
标签:Azides, TAMRA (TMR, tetramethylrhodamine),叠氮化物,Dye azides
| 货号 | 规格 | 价格 | 货期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| A7130 | 1 mg | 110.00$ | in stock |
| B7130 | 5 mg | 180.00$ | 5 days |
| C7130 | 10 mg | 310.00$ | in stock |
| D7130 | 25 mg | 410.00$ | in stock |
| E7130 | 50 mg | 695.00$ | in stock |
| F7130 | 100 mg | 1190.00$ | in stock |
TAMRA (TMR, tetramethylrhodamine) azide, solid compound, and 10 mM solution in DMSO, labeling reagent for Click Chemistry. Pure 5-isomer.
TAMRA is often used as FRET acceptor for FAM fluorophore.
TAMRA(TMR,四甲基罗丹明)叠氮化物、固体化合物和 10 mM DMSO 溶液,Click Chemistry 的标记试剂。 纯5-异构体。
TAMRA 通常用作 FAM 荧光团的 FRET 受体。
Can replace DyLight 549.
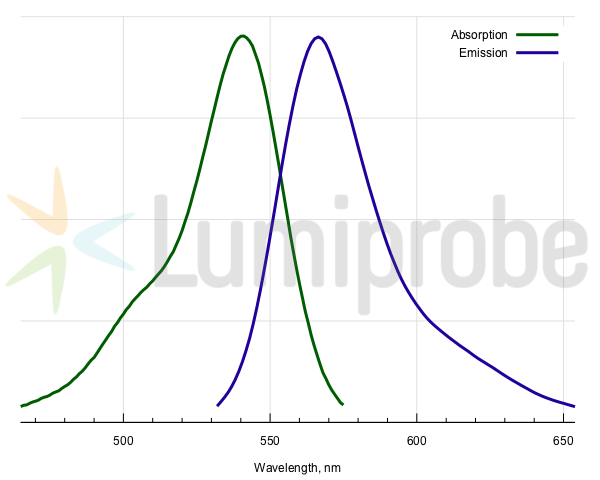
Absorption and emission spectra of 5-TAMRA
TAMRA azide, 5-isomer,叠氮化物,Dye azides相关产品
Sulfo-Cyanine3 maleimide
Water soluble thiol-reactive derivative of Sulfo-Cyanine3, a Cy3 analog.
Sulfo-Cyanine3 的水溶性硫醇反应性衍生物,一种 Cy3 类似物。
dsGreen Gel Staining Solution, 10000×
dsGreen for staining dsDNA in gels.
dsGreen 用于在凝胶中染色 dsDNA。
FAM azide, 5-isomer
FAM (fluorescein) azide for Click chemistry, pure 5-isomer.
用于点击化学的 FAM(荧光素)叠氮化物,纯 5 异构体。
General properties
| Appearance: | violet solid / solution 紫色固体/溶液 |
| Mass spec M+ increment: | 512.2 |
| Molecular weight: | 512.56 |
| CAS number: | 825651-66-9 |
| Molecular formula: | C28H28N6O4 |
| Solubility: | good in polar organic solvents (DMF, DMSO, alcohols), low in water |
| Quality control: | NMR 1H, HPLC-MS (95%) |
| Storage conditions: | Storage: 24 months after receival at -20°C in the dark. Transportation: at room temperature for up to 3 weeks. Avoid prolonged exposure to light.
储存:收到后 24 个月,在 -20°C 避光保存。 运输:在室温下长达 3 周。 避免长时间暴露在光线下。 |
| MSDS: | Download |
| Product specifications |
Spectral properties
| Excitation/absorption maximum, nm: | 541 |
| ε, L⋅mol−1⋅cm−1: | 84000 |
| Emission maximum, nm: | 567 |
| Fluorescence quantum yield: | 0.1 |
| CF260: | 0.32 |
| CF280: | 0.19 |
相关文献:
- Petrunina, N.A.; Lebedev, V.V.; Kirillova, Y.G.; Aralov, A..V.; Varizhuk, A.M.; Sardushkin, M.V. DNA Intercalated Motifs with Non-Nucleoside Inserts. Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry, 2021, 47(6), 1341–1344. doi: 10.1134/S1068162021060212
- Puthenveetil, R.; Lun, C.M.; Murphy, R.E.; Healy, L.B.; Vilmen, G.; Christenson, E.T.; Freed, E.O.; Banerjee, A. S-acylation of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein: Mechanistic Dissection, In Vitro Reconstitution and Role in Viral Infectivity. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2021, 297(4), 101112. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101112
- Seneviratne, U.; Huang, Z.; Am Ende, C.W.; Butler, T.W.; Cleary, L.; Dresselhaus, E.; Evrard, E.; Fisher, E.L.; Green, M.E.; Helal, C.J.; Humphrey, J.M.; Lanyon, L.F.; Marconi, M.; Mukherjee, P.; Sciabola, S.; Steppan, C.M.; Sylvain, E.K.; Tuttle, J.B.; Verhoest, P.R.; Wager, T.T.; Xie, L.; Ramaswamy, G.; Johnson, D.S.; Pettersson, M. Photoaffinity Labeling and Quantitative Chemical Proteomics Identify LXRβ as the Functional Target of Enhancers of Astrocytic apoE. Cell Chemical Biology, 2021, 28(2), 148–157.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.09.002
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, M.; Xu, Y.; Komaniecki, G.P.; Kosciuk, T.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Zou, X.; Linder, M.E.; Lin, H. A STAT3 palmitoylation cycle promotes TH17 differentiation and colitis. Nature, 2020, 586(7829), 434–439. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2799-2